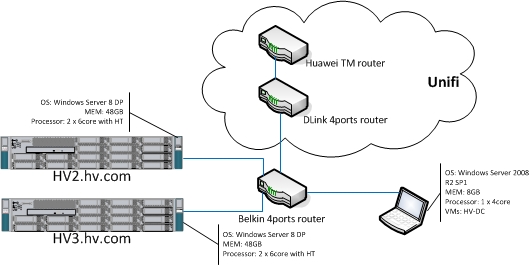
·
Increased
App Owner agility with self-service interface
·
It saves
time by bringing together all delegated infrastructure
·
It
improves reliability by deploying template-based services
App Controller presents a customized view
based on your security credentials, so you’ll see exactly how much of the
corporate resources have been dedicated to you regardless of their actual
location. In other words, it’s virtualized so it’s physical placement doesn’t
matter anymore. This view spans
multiple VMM servers and also incorporates Azure subscriptions, so you can
really manage your services without caring anymore about the underlying
resources. You know how much capacity
you have, in terms of network, storage and compute, and you can deploy services
against it which allows you to save time and increase agility (response time).
You can deploy services based on pre-configured templates as well.
Orchestrator
Orchestrator is simply
a process automation and integration engine. It offers workflow integration and
3rd party integration. On top of that, it comes with simple design
of custom workflow runbooks and integration packs (from application vendors).
The benefits of
Orchestrator are abundant and one of it is that by automating repetitive tasks,
it lowers cost and increases reliabilities. Besides, it also simplifies
heterogeneous datacenter management.
Orchestrator leverages a simple graphical
interface to construct custom workflows – with no codes required whatsoever. It also comes with Integration Packs designed
for the largest 3rd party datacenter management solutions such as
BMC, HP, Tivoli and even VMware. The good news is, if the Integration Pack
isn’t available, you’re able to easily design a custom one of your own.
Virtual
Machine Manager
System Center 2012 has the ability to work in
heterogeneous environments.
Specifically, VMM is able to manage all three major hypervisors –
Hyper-V, Xen Server & ESX. This
means that you can leverage what you already own in creating a more productive
infrastructure without having to decommission your existing virtualization
infrastructure, which can be extremely costly. VMM in SC2012 is built with a
“leverage existing TCO, and yield better ROI” thing in mind.
VMM now contains a feature called Server
Application Virtualization (SAV) which allows for the separation of the
application state from the underlying operating system. That simply said, instead
of having a custom deployment for each application, now you can keep your core
OS and SQL images in a library and then compile the service at run time. Then when the OS needs to be updated, you
simply update the library image and it will proliferate to all of the services
built off that image.
Finally, VMM offers Dynamic Optimization, a
feature that looks across your resources every 60 seconds and then, based on
policy, will either consolidate or spread the load to meet your specifications
and this is all done with Live Migration!
Configuration
Manager
With this release of SC2012 we are now able to
actually remediate against problems automatically which continues to increase
compliance and uptime in our environment, be it in a datacenter, private or
public clouds.
The Configuration Manager in SC2012 integrates
the management of System Center Endpoint Protection (formerly as Forefront
Endpoint Protection). This is
significantly crucial as most organizations have two entirely different
infrastructures to manage the configuration/state of the client devices and the
security of those devices. By leveraging
Endpoint Protection, you can virtually eliminate that second physical
infrastructure.
Amongst the benefits of Configuration Manager
in SC2012 are:
·
It reduces compliance complexity
·
It improves support for
virtualized environments
·
It reduces cost through integrated
security
Service
Manager
System Center Service Manager is the process
management hub which adapts the ITIL and MOF practice. New in SC2012 are the
service catalog, self-service request portal, release and SLA management and
the data warehousing and reporting capabilities.
Self-Service is a key principle of cloud
computing, this is how the Service Consumer will request cloud capacity or a
specific VM
Benefits of Service Managers are;
·
Increased organizational agility
with customized service offerings
·
Improved corporate compliance
through process management
·
Improved business intelligence
through customized reporting i.e. Excel spreadsheet reporting support
Operation
Manager
We can now have deep application insight,
which is the ability to monitor applications and if performance is less than
expected, we can actually see the line of code that is causing the problem and with
the plug in for Visual Studio Team System, we can immediately send it over to
development as a work item. This speeds up problem remediation considerably,
thereby complying with SLA and doesn’t put our up time in any jeopardy
whatsoever.
Also, Operation Manager now extends the monitoring
functionality to the cloud by offering a management pack that allows us to
monitor Windows Azure Applications as well (available for download on the
System Center Marketplace).
Now we can not only monitor Windows
installations, but also the UNIX and LINUX deployments. We also can monitor the
network layer for the health status of all key pieces of the infrastructure.
The last item to note is the introduction of
custom dashboards that can exist in the console on the web or in a SharePoint
deployment and we can have custom views designed for different people based on our
log in security credentials (username & password).
The benefits of Operation Manager in SC2012
are:
·
Simplified management with
visibility across the stack
·
Decreased time to resolution with
deep application insight
·
Improved insights with
customized/personalized reporting
Data
Protection Manager
Data Protection Manager 2012 enables
continuous data protection of Microsoft application, virtualization and file
servers to seamlessly integrated secondary disk, tape, and cloud. It is built
for enterprise scale.
Built on Operations Manager technology, DPM
offers a new console that provides centralized monitoring, management, and
troubleshooting of servers. From this single console, we can perform the same
protection, infrastructure management, troubleshooting, and reporting tasks as
we did for a single Data Protection Manager server using the administrator
console.
DPM is designed to protect and recover data
from applications such as: Windows file shares, client data, and system state;
Hyper-V technologies; SQL servers; Sharepoint and Microsoft Exchange Server.
Another new functionality in DPM 2012 is the
improved support in diverse environments. If we are running virtualized
servers, DPM 2012 enables Hyper-V Item Level Recovery even when it’s running
inside a VM.
DPM 2012 protects against generic data
sources. It provides basic protection and recovery of any referential data
sources, full backup (express, full, delta replication, and consistency check)
for any application. It also supports the protection on the use of XML for
applications that do not have a Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) writer. Last
but not least, original location recovery and restoring files to a network
location are feasible with DPN 2012 comes with SC 2012.
Try out our SC2012 labs on
For more info on SC2012 & the Evals
download, please go to
To learn more about other MS products, please go
to